Home > Products > Thermocouples & RTDs > Thermocouple Color Codes / Conductor Combinations & Characteristics

Below is a chart of the thermocouple codes/conductor combinations per different countries and their characteristics. Countries listed in this chart include: United States of America, United Kingdom, Germany, Japan, and France.
Thermocouple codes in this chart include: K, V, T, J, E, N, R, S, B, U, W, W5, and W3.
Code | Conductor Combinations | Approximate Generated EMF Change per Degree F change with Reference Junction at 0°F µV / °F at... | Approximate Working Temperature Range of Measuring Junction °F | National Standards for Output of Thermocouple Conductors (Those standards noted in this column all conform with each other and are based upon IPTS 1968 & IEC 584.1:1977.) |  American |  English to BS1843 |  German to DIN 43714 |  Japanese |  French to NR C 42-323 | Notes |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
+ leg | - leg | 212°F | 932°F | 1832°F | Continuous | Short Term | ||||||||
K | Nickel-Chromium Also known as: Chromel, Ni-Cr, T1 | Nickel-Aluminum Also known as: Ni-Al, Alumel, KN, T2 | 23.33 | 23.89 | 21.67 | 32 to +2012 | -292 to +2462 | ANSI/MC96.1 Type "K" | 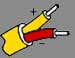 | 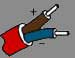 | 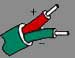 |  | 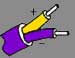 | Wide range and most commonly used. ANSI/MC96.1 Type "K" replaced circular 561. |
V | Copper | Copper-Nickel Also known as: Constantan, Nickel | Used for interconnecting Type "K" thermocouples and instrumentation as an alternative to Type "K" material. Only used where the interconnection temperature is in the range of 32°F to +176°F |  |  |  | Color coded for use as a compensating cable for Type "K" thermocouples. This compensating cable can also be used for extending Type "T" thermocouples. |
|||||||
T | Copper | Copper-Nickel Also known as: Nickel, Cupron, Constantan | 25.55 | -301 to +572 | -328 to +662 | ANSI/MC96.1 Type "T" |  |  |  |  |  | Many low temperature and cryogenic applications. Suitable for use in a mildly oxidizing or reducing atmosphere as an unprotected thermocouple sensor. ANSI/MC96.1 Type "T" thermocouple replaced circular 561. |
||
J | Iron (magnetic) Also known as: FE | Copper-Nickel Also known as: Constantan, Cupron | 25.55 | 31.11 | 32.78 | +68 to +1292 | -292 to +1382 | ANSI/MC96.1 Type "J" |  | 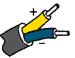 | 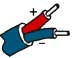 | 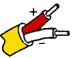 | 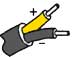 | Commonly used in the plastic molding industry. Used in reducing atmospheres as an unprotected thermocouple sensor. NB Iron rusts at low and oxidizes at high temps. ANSI/MC96.1 Type "J" replaced circular 561. |
E | Nickel-Chromium Also known as: Chromel, Chromium Nickel | Copper-Nickel Also known as: Nickel Copper, Constantan | 37.78 | 45.00 | 32 to +1472 | ANSI/MC96.1 Type "E" |  |  |  |  | Highest thermal EMF output change/°F. Suitable for use in a vacuum or mildly oxidizing or reducing atmosphere as an unprotected sensor. ANSI/MC96.1 Type "E" replaced circular 561. |
|||
N | Nickel-Chromium Silicon Also known as: Nicrosil | Nickel-Silicon-Magnesium Also known as: Nisil | 16.67 | 21.11 | 21.67 | 32 to +2012 | -450 to +2372 | This combination shows good promise as an alternative to Type "K". Appears to be more stable and longer-lived. |
||||||
R | Platinum- 13% Rhodium | Platinum | 4.45 | 5.56 | 7.23 | 32 to +1600 | -58 to +3092 | ANSI/MC96.1 Type "R" |  |  |  | Used for high temp applications. Has high resistance to oxidation and corrosion. Easily contaminated and normally requires protection. ANSI/MC96.1 Type "R" replaced circular 561. |
||
S | Platinum- 10% Rhodium | Platinum | 4.45 | 5.00 | 6.11 | 32 to +2822 | -58 to +3092 | ANSI/MC96.1 Type "S" |  |  |  |  |  | See Type "R". ANSI/MC96.1 Type "S" replaced circular 561. |
B | Platinum- 30% Rhodium | Platinum- 6% Rhodium | 0.56 | 2.78 | 5.00 | +212 to +2912 | +122 to +3182 | ANSI/MC96.1 Type "B" |  |  |  | See Type "R". Commonly used in glass industry. Copper vs copper compensating cable can be used to normal ambient interconnection temps up to 100°C. ANSI/MC96.1 Type "B" replaced circular 561. |
||
U | Copper | Copper-Low Value Nickel Also known as: Nickel | Used for interconnecting Type "R" and "S" thermocouples and instrumentation. Only used where the interconnection temperature is in the range of 32°F to +122°F. |  |  |  |  |  | This is a compensating cable only and is used with Types "R" and "S" measuring thermocouple sensors. |
|||||
W | Tungsten | Tungsten- 26% Rhenium | 2.78 | 8.89 | 11.67 | +68 to +4172 | 32 to +4712 | Tungsten Rhenium alloy combinations offer reasonably high and relatively linear EMF outputs for high temp measurement up to 4712°F and good chemical stability at high temps in hydrogen, inert gas, and vacuum atmospheres. They are not really practicable for use below 752°F. Not recommended for use in oxidizing conditions. Suggested compensating cables are listed below. |
||||||
W5 | Tungsten- 5% Rhenium | Tungsten- 26% Rhenium | 8.34 | 10.00 | 10.00 | +68 to +4172 | 32 to +4712 | |||||||
W3 | Tungsten- 3% Rhenium | Tungsten- 25% Rhenium | 7.23 | 11.11 | 11.11 | +68 to +3632 | 32 to +3812 | |||||||
Thermocouple Combinations | Compensating Cable | Combination |
+ leg | - leg |
|
W | ALLOY 200 | ALLOY 226 |
W5 | ALLOY 405 | ALLOY 426 |
W3 | ALLOY 203 | ALLOY 225 |
Written by Shelby Reece
Date Published: 12.10.2018
Last Updated: 03.12.2020
